Anti-inflammatory diet keeps you muscular and strong
Not only a diet with enough protein can help you stay muscular and strong after your fifties. Nutritional ingredients that you probably do not directly associate with muscle or strength, such as fish oil, tea, thyme, selenium and vitamin C, can contribute as well. Iranian scientists report in Nutrition Journal that a diet with a low dietary inflammatory index reduces the risk of sarcopenia - or age related, involuntary loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]

[FONT="]
[/FONT]
Study
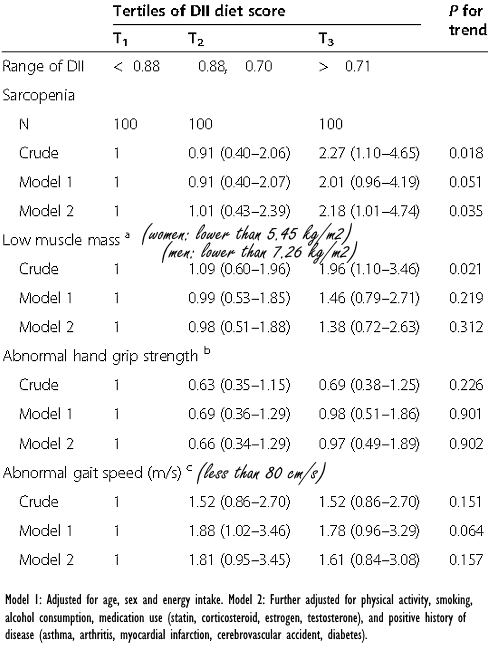
The researchers, who are affiliated with Tehran University of Medical Sciences, measured the muscle mass, strength and daily functioning of 150 men and 150 women over 55. At the same time, the researchers determined the dietary inflammatory index of the diet of the study participants.Sugars, industrially processed foods and even more nutritional components known as 'unhealthy' increase the dietary inflammatory index. Food components with the opposite effect include unsaturated fatty acids, fiber, magnesium, beta-carotene, vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, B11, C, D, E, anthocyanidins, flavanols, flavonols, flavanones, flavones, isoflavones, garlic, ginger, pepper, onions, tea, eugenol, saffron, selenium, turmeric, zinc, thyme, oregano and rosemary.
Here you can read more about the concept of the dietary inflammatory index.
Results
The trend was that a diet with a relatively low dietary inflammatory index had a positive effect on muscle mass, strength, speed and everyday functioning. However, these associations were not significant.
The researchers then determined whether there was sarcopenia by combining all these factors (muscle mass, strength, etc.) and found that the association between sarcopenia and dietary inflammatory index was statistically significant.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
[FONT="]
[/FONT]
"Greater adherence to a diet with more pro-inflammatory properties was associated with increased odds of sarcopenia in older adults", the Iranians summarize their findings.
"These findings support the current dietary recommendations on reducing the consumption of unhealthy foods with pro-inflammatory properties to reduce the risk of several chronic conditions including sarcopenia."
Source:
Nutr J. 2020 Nov 28;19(1):129.
Not only a diet with enough protein can help you stay muscular and strong after your fifties. Nutritional ingredients that you probably do not directly associate with muscle or strength, such as fish oil, tea, thyme, selenium and vitamin C, can contribute as well. Iranian scientists report in Nutrition Journal that a diet with a low dietary inflammatory index reduces the risk of sarcopenia - or age related, involuntary loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]

[FONT="]
[/FONT]
Study
Here you can read more about the concept of the dietary inflammatory index.
Results
The trend was that a diet with a relatively low dietary inflammatory index had a positive effect on muscle mass, strength, speed and everyday functioning. However, these associations were not significant.
The researchers then determined whether there was sarcopenia by combining all these factors (muscle mass, strength, etc.) and found that the association between sarcopenia and dietary inflammatory index was statistically significant.
[FONT="]
[/FONT]

[FONT="]
[/FONT]
"Greater adherence to a diet with more pro-inflammatory properties was associated with increased odds of sarcopenia in older adults", the Iranians summarize their findings.
"These findings support the current dietary recommendations on reducing the consumption of unhealthy foods with pro-inflammatory properties to reduce the risk of several chronic conditions including sarcopenia."
Source:
Nutr J. 2020 Nov 28;19(1):129.


